

Fas-induced activation of the cell death-related protease CPP32 is inhibited by Bcl-2 and by ICE family protease inhibitors. Caspase activity is required for commitment to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Sequential activation of ICE-like and CPP32-like proteases during Fas-mediated apoptosis. Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Cell nucleus and DNA fragmentation are not required for apoptosis. Schulze-Osthoff, K., Walczak, H., Dröge, W. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis.
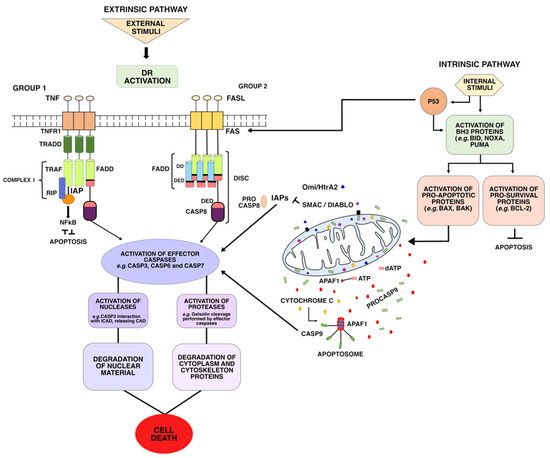
Identification of deoxyribonuclease II as an endonuclease involved in apoptosis. Potential roles of cyclophilins in apoptosis. Native recombinant cyclophilins A, B, and C degrade DNA independently of peptidylpropyl cis-trans-isomerase activity. Characterization of the endogenous deoxyribonuclease involved in nuclear DNA degradation during apoptosis (programmed cell death). Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. Abiochemical hallmark of apoptosis: internucleosomal degradation of the genome. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Programmed cell death in animal development. ICAD therefore seems to function as a chaperone for CAD during its synthesis, remaining complexed with CAD to inhibit its DNase activity caspases activated by apoptotic stimuli then cleave ICAD, allowing CAD to enter the nucleus and degrade chromosomal DNA. When CAD is expressed with ICAD in COS cells or in a cell-free system, CAD is produced as a complex with ICAD: treatment with caspase 3 releases the DNase activity which causes DNA fragmentation in nuclei. Recombinant ICAD specifically inhibits CAD-induced degradation of nuclear DNA and its DNase activity. CAD is a protein of 343 amino acids which carries a nuclear-localization signal ICAD exists in a long and a short form. A caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD) and its inhibitor (ICAD) have now been identified in the cytoplasmic fraction of mouse lymphoma cells. Apoptosis is mediated by members of the caspase family of proteases, and eventually causes the degradation of chromosomal DNA. The homeostasis of animals is regulated not only by the growth and differentiation of cells, but also by cell death through a process known as apoptosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
